





ANTI-TIGIT ANTIBODY
ABOUT TIGIT: TIGIT is a checkpoint receptor expressed on immune cells, including T cells and NK cells, that inhibits the immune system’s natural ability to detect and kill cancer cells. It binds CD155 on tumor cells preventing its interaction with CD226, resulting in suppression of the immune system’s ability to attack cancer.
TIGIT is co-expressed with PD-1 on tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes or NK cells and has been associated with poor prognosis in a variety of cancers.
TIGIT and PD-1 have distinct, non-redundant functions in controlling antitumor immune responses. Preclinical studies have shown synergistic antitumor activity with combined inhibition of TIGIT and PD-1.
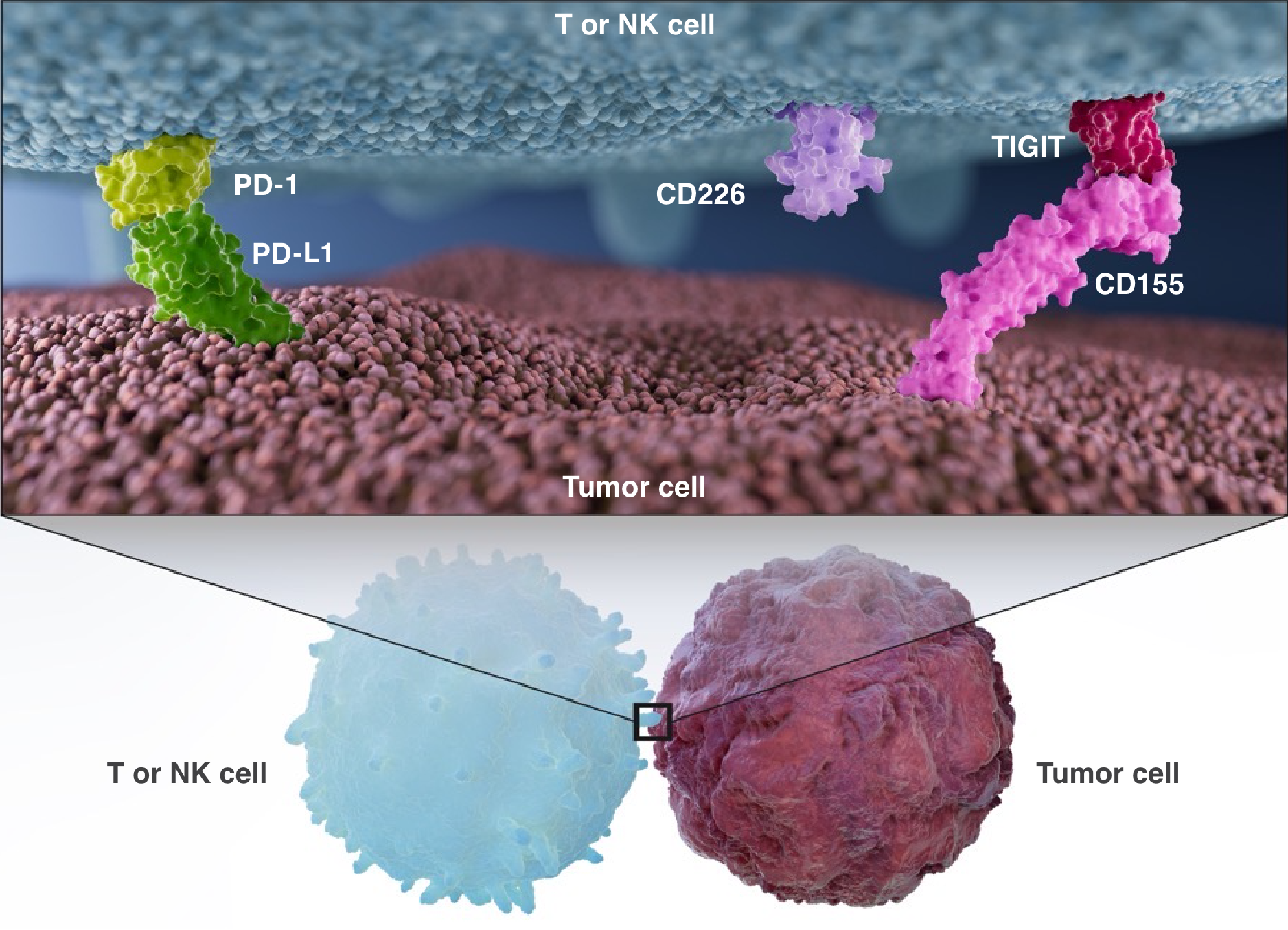
Immunosuppression
PD-L1 expressed on tumor cells binds to the checkpoint receptor PD-1 on T and NK cells and leads to immunosuppression.
TIGIT is another checkpoint receptor expressed on immune cells that binds CD155 on tumor cells, leading to further evasion of antitumor immunity.
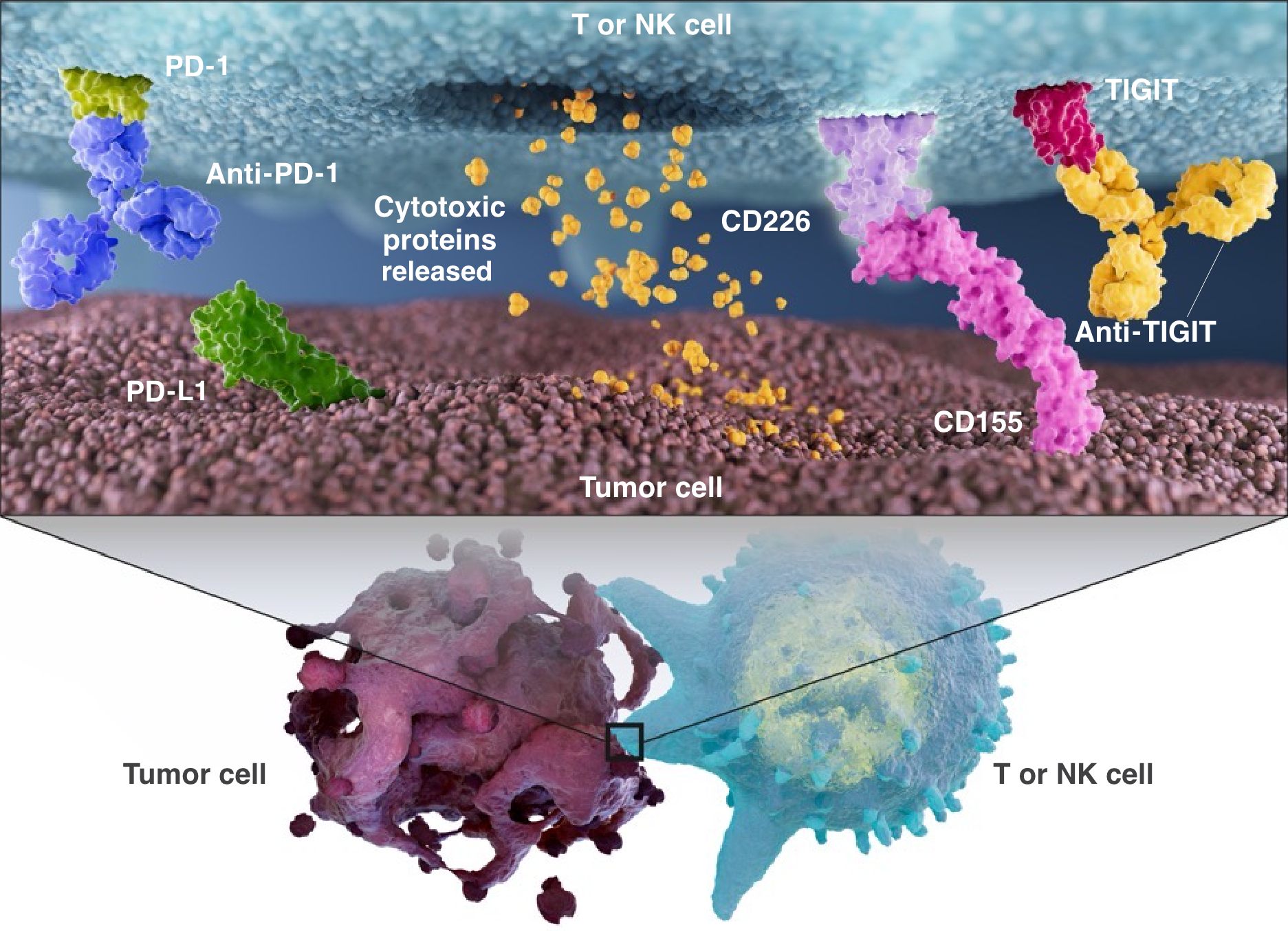
Immune Cell Activation & Tumor Cell Killing
Combined inhibition of TIGIT and PD-1 may have a synergistic effect to unleash robust immune activity against certain tumor cells.
In preclinical studies, dual TIGIT and PD-L1 blockade resulted in increased tumor cell killing and longer survival.
Arcus is developing domvanalimab (dom), an Fc-silent investigational monoclonal antibody that binds to TIGIT and may enable CD155:CD226 interaction and subsequent immune cell activation.
